Our Location Data
We turn raw location data from millions of global mobile devices into enterprise location intelligence.
Location intelligence is essential data for any organization that needs to know how people, products, and materials move around the world.
We produce the highest quality location data in the industry.
Our AdmitOne processing engine uses Location Data Forensics to filter and categorize location signals, ultimately verifying consumer visits to millions of places and events. Our enterprise location intelligence delivers indispensable and privacy-friendly insight into consumer movement, interests, and intent. Read on to find out more about how we create our data.
The Growing Location Intelligence Industry
According to eMarketer’s report, Location Intelligence 2022, the location intelligence market opportunity is already more than $10 billion globally, and it is projected to grow to $20 billion by the middle of the decade. This double-digit growth is driven by the rapid adoption of location intelligence solutions by leading companies around the world.
By using location data to gain insight into human mobility, companies across industries gain valuable insight into their markets, customers, and competitors. This data can be used in many different ways. For example, financial institutions may use location data to figure out how well a company is doing based on foot traffic, while a store can use the same data to decide where to open its next store. Transportation and logistics providers can use this data to understand common routes or travel patterns in an area, while a travel or tourism company might use it to understand how far its visitors travel or to improve its marketing strategies. What’s more, new use cases for location intelligence and the insights that location data provides are still emerging.
In fact, 9 out of 10 companies worldwide that are currently using location data expect its use to only become more important in the coming years.
Why Purchase Location Data?
When location data is properly cleansed and given the right context, it can be used to build new data products that help businesses improve their marketing and sales strategies and optimize business operations. Today, location intelligence is used to power cutting-edge solutions in many industries that need to know how people, goods, and materials move around the world.
| Market Research | Digital Advertising | Competitive Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Uncover new consumer trends and priorities in your market with in-depth foot traffic insights. | Reach more engaged and in-market consumers with advertising audiences built on location data. | Use location data to compare your company’s performance against competitors in your industry. |
| Operational Intelligence | Site Selection | Data Enrichment |
|---|---|---|
| Improve your business processes with real-world insight into consumer movement. | Understand consumer behavior and foot traffic patterns by time-of-day or day-of-week at any location of interest. | Enrich your first-party customer data with location-based insights to improve segmentation and targeting. |
But using location intelligence successfully in your business starts with having high-quality location data to work with. At Gravy, we’re proud to produce the highest quality data in the industry.
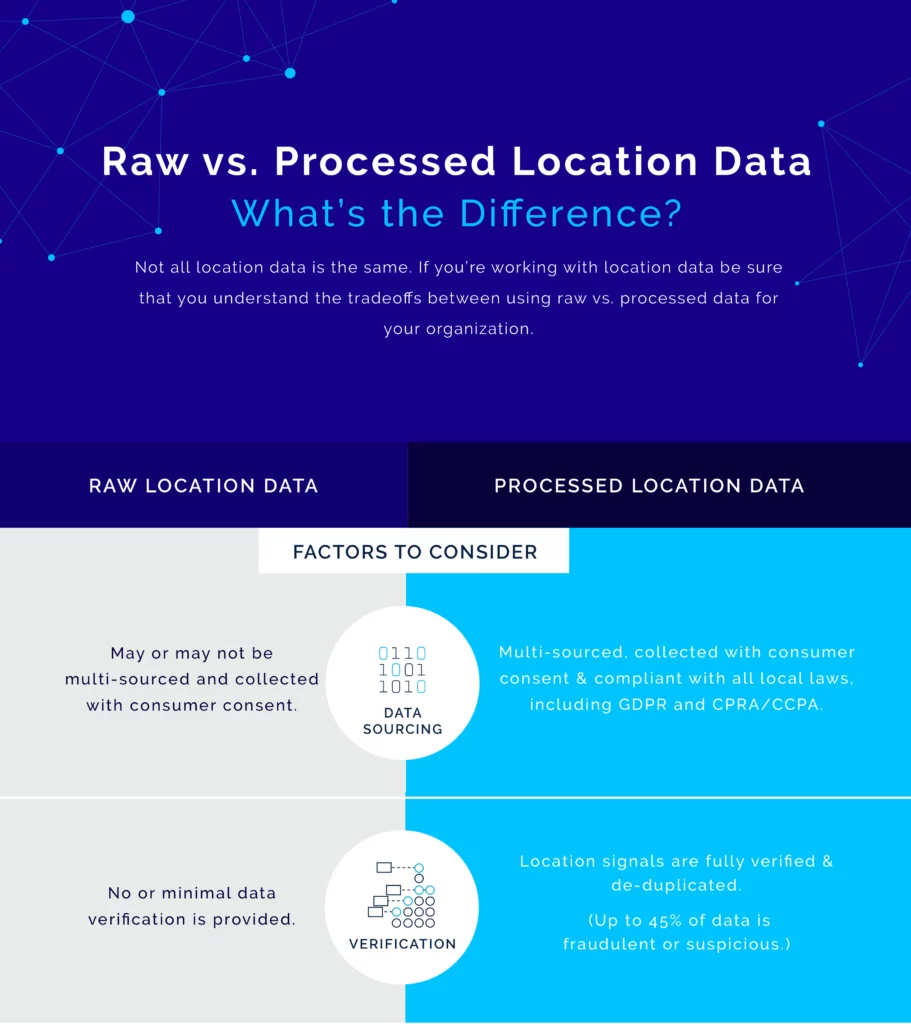
What’s the difference between first- and third-party location data?
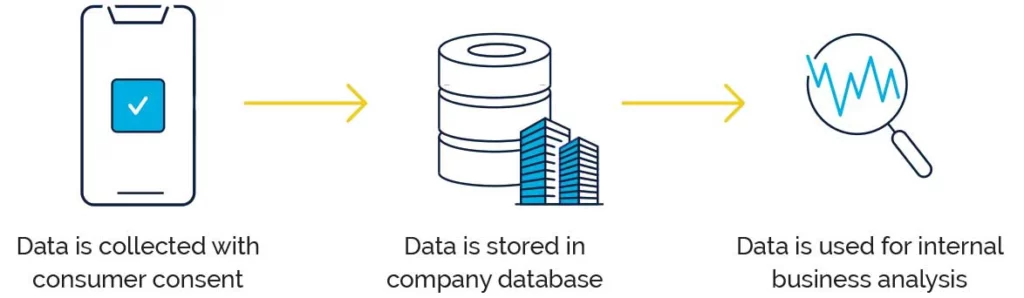
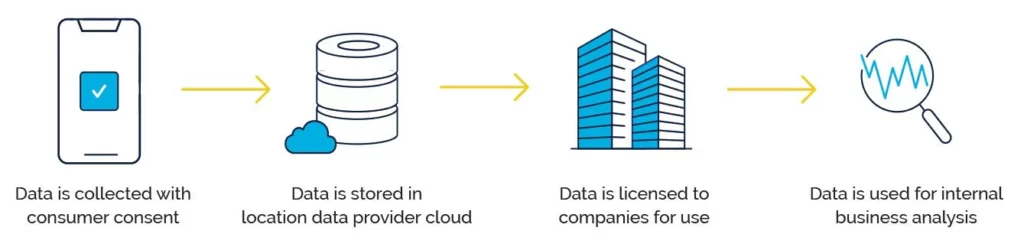
First-party location data is information that a business or app developer collects as a byproduct of serving its customers. A business or app developer may also package and license its data to other businesses as third-party data. In both cases, the data is collected with consumer consent. Both first- and third-party data will include a device identifier, latitude, longitude, and timestamp. The key difference is that some app developers or companies only ask for permission to collect and use their customers’ location data for internal analysis, while others ask for permission to share the data they collect with others.
First-Party Location Data
Third-Party Location Data
Both first-party location data and third-party location data are useful. For example, a company can use its own first-party location data to figure out what its customers are most interested in by analyzing the types of places they go in the physical world. A company might also use its own location data to create an advertising audience of its current customers or to understand how far they travel to visit one of its stores. For a larger-scale location analysis that looks at how its competitors’ customers act or how the general population in an area lives, however, the company will most likely need to buy data from a reputable third-party location data provider as well.
Why might a company need to purchase more location data? By definition, the location data that most companies collect shows how their customers act, not how everyone in the world acts. Location data providers work with a lot more location data, which represents a lot more consumer devices and a wider range of consumers. Location data companies are, of course, the best place for companies that don’t collect their own location data to get this kind of information. But companies that do have 1st-party data often find that having 3rd-party data to work with as well makes their 1st-party data more usable for analysis.
Purchasing data from a location data provider has another advantage: not only do these companies work with location data at scale, but they also provide support services tailored to their clients’ business needs.
Factors to Consider When Purchasing Location Data
Location data providers know a lot about location technology and, in particular, how to process data. They work hard to make sure that the data they collect complies with all local laws, and they pay a lot of attention to the data’s reliability and coverage. Here are just a few of the ways that a location data provider can help your organization get the most from location data.
| Factors to Consider | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Records | Name, signature, social security number, physical characteristics or description, address, telephone number, passport number, driver's license or state identification card number, insurance policy number, education, employment, employment history, bank account number, credit card number, debit card number, or any other financial information, medical information, or health insurance information. |
| Aggregated Data | Location data providers collect information from millions of mobile devices and thousands of different apps. This lets organizations work with location data on a scale that is more representative of the population. |
| Data Processing | Some location data providers provide data cleansing and deduplication services, improving the quality of the data and making it easier for organizations to start using the data for analysis. |
| Data Enrichment | Location data providers can add data from other sources, like demographic or census data, to give location signals more context and provide more meaningful analysis. |
| On-Demand Analytics | Some location data providers offer pre-built analytics and derivative datasets that make it easier for companies to get started with location-based analytics and insights. |
Location data providers not only give you access to large amounts of high-quality data, but they also give you access to know-how and best practices that can only be learned through years of experience working with this data in the real world. Still, it is important to evaluate the offerings of each provider to determine which is the best fit for your organization. Some location data providers offer professional services that are tailored to the needs of businesses, while others offer specialized geospatial software solutions that are tailored to a certain industry. For companies that have their own first-party location data but are not yet using it for business intelligence, a location data provider may be able to help clean up the data and interpret its meaning so that it can be used for analysis.
No matter which option you choose, working with a location data provider can make it far easier for your business to get started with location intelligence and help you get the most from your location data investment.
The Enterprise Location Intelligence Company
As an enterprise location technology company, Gravy Analytics aims to be the largest and most trusted source of actionable location intelligence. Using its patented technology, Gravy Analytics combines billions of daily global location signals into a single, annotated location data stream before creating an array of datasets and analytics that are specially designed for enterprise applications.
How Raw Location Data Becomes Location Intelligence
Step 1. Raw location data is aggregated.
As an enterprise location intelligence company, Gravy works with a host of location data providers who have raw location data from thousands of different apps. This ensures a more consistent raw location data supply over time and a large-scale data sample that better represents the population.
Step 2. AdmitOne data processing starts.
To make raw location data usable for analysis, Gravy developed a patented data processing technology, AdmitOne. The AdmitOne platform processes billions of raw location signals every day, eliminating fraudulent, problematic, and duplicate data, and creating a unified, high-quality data stream.
Step 3. Location Data Forensics are added.
Location Data Forensics are added to each verified location signal, providing additional information about signal origin, location accuracy, and other key characteristics. Location forensics enable analysts to quickly segment data for analysis.
Step 4. Observations are created.
Observations are recorded, offering insight into human activity and people movement on a global scale. Our Observations data is the foundation of all of our location intelligence datasets and analytics.
Step 5. Observations are matched to places & events.
Observations are matched to precision geofences for millions of places, events, and points-of interest. While our geofences are primarily in the U.S. and Canada, new fences may be easily added for any place or event globally.
- 1M+ monthly events
- Millions of commercial places of interest
- Custom geo-areas
- Precise, polygonal geofences
Step 6. Visitations are calculated.
Visitations, consumer visits to a place or event likely to include a commercial transaction, are then recorded. Offering privacy-friendly insight into foot traffic at millions of places of interest, and thousands of top brands, Visitations is one of our most popular derivative datasets.
Step 7. Analytics & Audiences are built.
Observations & Visitations are the basis for our industry-leading data analytics and advertising audiences. Understand trade area, distance traveled, brands visited, and much more. Or, reach your target audiences based on places they go in the real world.
Location Data Products Designed for the Enterprise
Gravy Analytics offers a range of datasets, APIs, and advertising audiences built on location data, in addition to privacy-enhancing technology for companies that work with location data. Whether added to a data warehouse or embedded in a software platform, our datasets and APIs are truly made for the enterprise.
| Location Intelligence Data & APIs | Foot Traffic Data & APIs | Advertising Audiences |
|---|---|---|
| Understand global human movement patterns using privacy-friendly mobility data and APIs built on billions of daily location signals. | Measure foot traffic at commercial locations of interest with data and APIs built on 1B+ monthly visits to places and events across the U.S. and Canada. | Reach more engaged consumers and improve campaign ROI with advertising audiences built on the places and events people visit in the real world. |
| Privacy Enhancing Technology - PrivacyCheck |
|---|
| The first privacy-enhancing technology (PET) of its kind, PrivacyCheck identifies location data collected at sensitive places so that it can be deleted from your systems. |
Location Intelligence Case Studies
See how our customers have used Gravy’s location datasets and analytics to measure consumer activity at places and events of interest.
Ready to get started with location data?
If your business needs to purchase high-quality, reliable location data or analytics, let us know. Request a no-cost, no-obligation consultation with one of our location intelligence experts today.
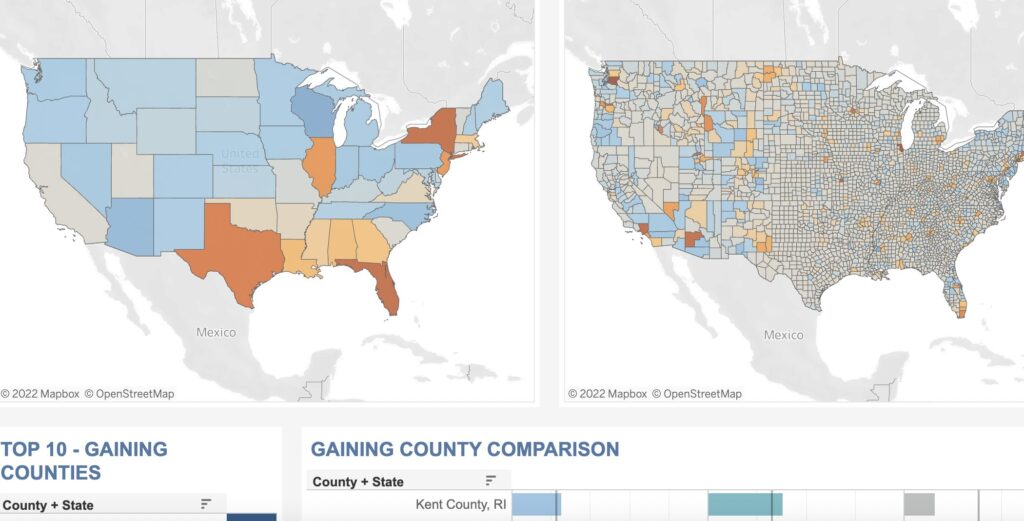
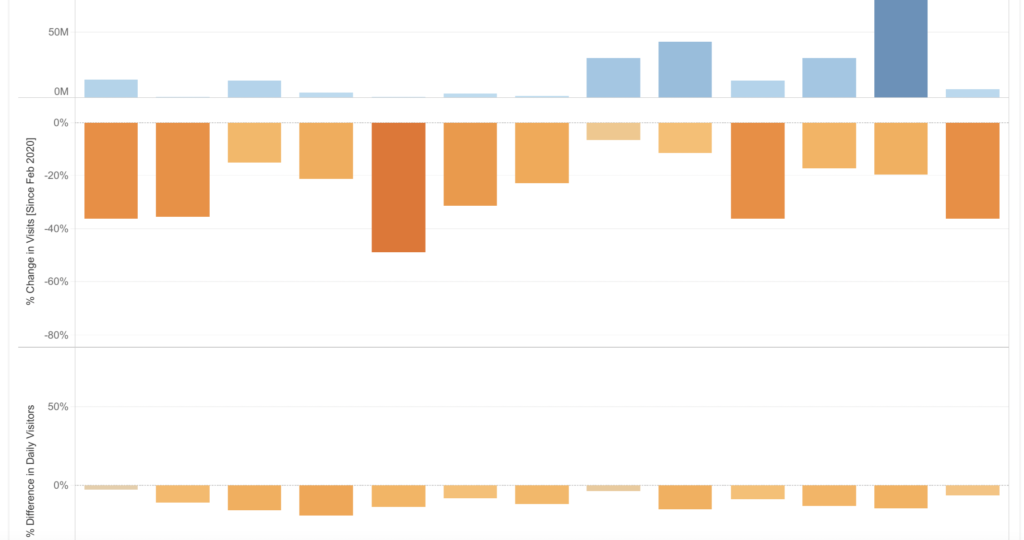
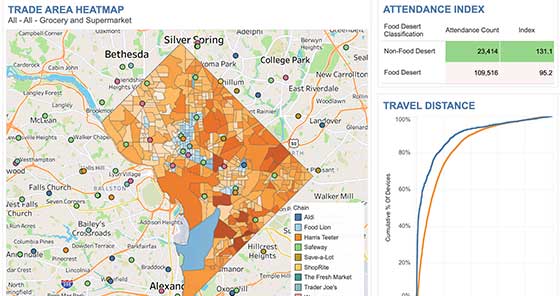
Visualizations Built on Location Data
The following dashboards use Gravy’s datasets to illustrate population distribution and consumer behavioral trends.